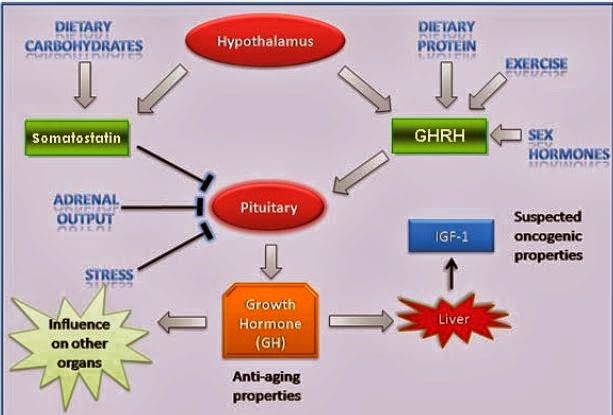
Crianças com baixa estatura e deficiência do hormônio do crescimento–hGH que é produzido na glândula pituitária, que está localizada na base do cérebro. A díade hipotálamo-hipófise é dos componentes mais complexos do sistema endócrino e neuroendócrino; é fundamental na coordenação de toda a resposta endócrina, estabelecendo relações de controle mútuo sobre a maioria das glândulas endócrinas, e controlando, por si só, muitos aspectos da homeostase corporal. Diferentes hormônios feitos no cérebro informam a glândula pituitária quanto o hormônio do crescimento GH é necessário. O hormônio do crescimento-hGH entra no sangue e estimula o fígado a produzir um hormônio chamado fator de crescimento insulina-símile 1 (IGF-1), que desempenha um papel chave no crescimento pós nascimento, mais específico em criança, infantil, juvenil. A altura anormalmente baixa na infância (chamado de baixa estatura) pode ocorrer se não houver produção suficiente do hGH-hormônio do crescimento. Na maioria das vezes, nenhuma causa clara da deficiência de hormônio do crescimento-hGH é encontrada e este fato recebe o nome de baixa estatura idiopática. Deficiência de hormônio do crescimento-DHGH pode estar presente ao nascimento (congênita). Pode também se desenvolver após o nascimento, como resultado de uma condição de lesão cerebral, tumor, causa idiopática e radiação na cabeça. Crianças com defeitos físicos da face e do crânio, como lábio leporino ou fenda palatina, são mais propensos a ter diminuição dos níveis de hGH-hormônio do crescimento. A deficiência de hormônio do crescimento-DHGH geralmente não é transmitida de pai para filho. Embora seja rara, a deficiência de hormônio do crescimento-DHGH também pode ser diagnosticada em adultos.
As possíveis causas incluem: cérebro que foi tratado com irradiação para o câncer pois tal pode comprometer o eixo hipotálamo-hipofisário, problemas hormonais envolvendo a glândula pituitária ou hipotálamo, ferimento grave na cabeça. Crianças com deficiência de hormônio do crescimento-DHGH têm um ritmo lento ou dificuldade regular de crescimento, crescem geralmente menos de 2 cm/ano, embora se compreenda que com deficiência de crescimento, criança, infantil, juvenil, adolescente em época de crescimento apresente valores de crescimento longitudinal inferior a 6 cm/ano, pois com certeza os pais esperam um possível estirão que poderá não acontecerá por todos os fatores descritos ou acontecerá em valores abaixo da expectativa, ou seja, cada individuo tem uma liberação de hGH-hormônio de crescimento em quantidades pessoais e individuais dependendo das variáveis únicas. O lento crescimento pode não aparecer até que a criança chegue aos 2 ou 3 anos de idade. A criança será muito menor do que a maioria das outras crianças ou de todas da mesma idade e sexo. Crianças com deficiência de hormônio de crescimento-DHGH ainda têm proporções normais do corpo, bem como a inteligência normal. No entanto, seu rosto tem aparência muitas vezes mais jovem do que crianças da mesma idade. Elas também podem ter um corpo gordinho para concluir a disfunção do déficit de GH. Em crianças mais velhas, a puberdade pode chegar mais tarde ou pode acontecer de não chegar a todos.
Todos esses desastres podem ser prevenidos se for muito bem observado precocemente e não pensar que é um estado passageiro que será compensado no futuro, o que normalmente não é verdade, e você terá filhos com baixa estatura com toda a certeza. E este fato se perpetuará na vida adulta também e não somente na fase de desenvolvimento de criança, infantil, juvenil.
SHORT STATUR-GROWTH; TIMING HYPOTHALAMIC-PITUITARY (PITUITARY), INTRAUTERINE, CHILD, CHILDREN AND YOUTH.
LOW
HEIGHT CHILDREN GROW : DISABILITY - HGH - GROWTH HORMONE : THE COMMAND
NEUROENDOCRINE THAT ESTABLISHES THE PITUITARY GLAND ( PITUITARY ) HYPOTHALAMUS
AND IS PART OF A SHAFT WITH STRONG INFLUENCE OF CORE ARCUATE WHAT ARE THE
BIGGEST SECRETORY RESPONSIBLE, FOR EFFICIENCY OR DISABILITY THE GH; PHYSIOLOGY-ENDOCRINOLOGY-NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY-ENDOCRINE-PEDIATRICS
(SUB- SPECIALTY ENDOCRINOLOGY): DR. JOÃO SANTOS CAIOJR. ET DRA. HENRIQUETA
VERLANGIERI CAIO.
BUT
PROSSEGE INSTALLING OR DEFICÊNCIA EFFICIENCY IN ENVIRONMENTAL AND EXTERNAL
FACTORS THAT CAN STILL GET INTRAUTERINE ( GENETICS ) UNTIL THE COMPLETION OF
PRE- LOAD PROGRAM AT EACH STAGE, CHILD, CHILDREN, YOUTH:
Children
with short stature and growth failure - hGH is produced in the pituitary gland,
which is located at the base of the brain hormone. The hypothalamic-pituitary
dyad is the most complex components of the endocrine and neuroendocryne system
, is crucial in coordinating the entire endocrine response , establishing
relationships of mutual control over most of the endocrine glands , and controlling
alone , many aspects of body homeostasis. Different hormones made in
the brain tell the pituitary gland as the growth hormone GH is necessary.
Growth hormone hGH - enters the blood and stimulates the liver to produce a
hormone called insulin growth factor -like 1 (IGF - 1), which plays a key role
in post birth, more specific growth in child, infant, child. The abnormally low
height in childhood (called short stature) may occur if there is insufficient
production of growth - hormone hGH. Most often, no clear deficiency of growth hormone,
hGH cause is found and this fact is called idiopathic short stature. Deficiency
of growth hormone - DHGH can be present at birth (congenital). It can also
develop after birth as a result of a condition of brain injury, tumor,
idiopathic and radiation to the head. Children of the face and skull physical
defects such as cleft lip or cleft palate are more likely to have decreased
levels of growth hormone - hGH. A deficiency of growth hormone - DHGH is
generally not transmitted from father to son. Although rare, deficiency of
growth hormone - DHGH can also be diagnosed in adults. Possible causes include:
the brain that was treated with radiation for cancer as this may compromise the
hypothalamic- pituitary axis, hormonal problems involving the pituitary gland
or hypothalamus, severe head injury. Children with growth hormone deficiency -
DHGH have a slow pace or regular failure to thrive, grow usually less than 2 cm/year,
while understandably with growth deficiency, child, infant, child, teenager
growing season in present values less than 6 cm/year longitudinal growth, for
surely parents can expect a growth spurt that may not happen for all the
factors described or held in values below expectation, i.e.,
each individual has a release of growth hormone hGH - personal and individual
quantities depending only variables. Slow growth may not appear until the child
reaches the 2 or 3 years old. The child will be much lower than most or all other
children of the same age and sex. Children with growth hormone deficiency -
DHGH still have normal body proportions and normal intelligence. However, his
face has often looks younger than children of the same age. They may also have
to complete a chubby dysfunction of GH deficit body. In older children, puberty
may arrive later or we may not arrive at all.
All these disasters can be
prevented if well observed early and do not think it is a temporary condition
which will be offset in the future, which is usually not true , and you will
have children with short stature with certainty. And this fact will be
perpetuated into adult life as well and not only at the stage of child
development, children and youth.
Dr. João Santos Caio Jr.
Endocrinologia – Neuroendocrinologista
CRM 20611
Dra. Henriqueta V. Caio
Endocrinologista – Medicina Interna
CRM 28930
1. Uma explicação possível é de que existam menos receptores de GH-hormônio de crescimento no feto quando comparados ao período pós-natal...
http://hormoniocrescimentoadultos.blogspot.com.
2. Estudos realizados em roedores, que não apresenta vários fatores de crescimento ou proteínas ligadoras, indicam uma função do IGF-2 (fatores de crescimento insulina-símile 2) sobre o crescimento durante o início da gestação...
http://longevidadefutura.blogspot.com
3. A inativação dos receptores tipo 1 de IGF-1 (fatores de crescimento insulina-símile 1) leva a uma falha de crescimento mais pronunciada do que encontramos nos ratos IGF-1 (fatores de crescimento insulina-símile 1), sugerindo que outros fatores além do IGF-1 (por exemplo, o IGF-2) exercem efeito sobre o crescimento fetal através do receptor tipo 1...
http://imcobesidade.blogspot.com
AUTORIZADO O USO DOS DIREITOS AUTORAIS COM CITAÇÃO
DOS AUTORES PROSPECTIVOS ET REFERÊNCIA BIBLIOGRÁFICA.
Referências Bibliográficas:
Caio Jr, João Santos, Dr.; Endocrinologista, Neuroendocrinologista, Caio, H. V., Dra. Endocrinologista, Medicina Interna – Van Der Häägen Brazil, São Paulo, Brasil; Selye, Hans (1974). Estresse sem angústia . Philadelphia: Lippincott; MacHale SM, Cavanagh JT, Bennie J, Carroll S, Goodwin GM, Lawrie SM (Novembro de 1998) "Variação diária da atividade adrenocortical na síndrome da fadiga crônica" . Neuropsychobiology38 (4):. 213-7 doi : 10,1159 / 000026543 . PMID 9813459 ; Backhaus J, K Junghanns, Hohagen F (outubro de 2004) "Os distúrbios do sono estão relacionadas com a diminuição da manhã despertar cortisol salivar" . Psiconeuroendocrinologia 29 (9):. 1184-1191 doi : 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2004.01.010 . PMID 15219642 ; Pruessner JC, Hellhammer DH, Kirschbaum C (1999) "Burnout, estresse percebido, e de cortisol respostas a despertar" . Psychosom Med 61 (2):. 197-Robert L. Spencer, Kent E. Hutchinson, álcool, envelhecimento e da resposta ao estresse , álcool Pesquisa e Saúde, Inverno 1999. pariante, CM (2003). . "Depressão, Stress e do eixo adrenal" Jornal de Neuroendocrinologia 15 (8): 811-812. doi : 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2003.01058.x . PMID 12834443 ; Douglas A (2005). "mecanismos noradrenérgicos centrais subjacentes respostas de estresse agudo do eixo hipotálamo-hipófise-adrenal:. adaptações durante a gravidez e lactação". Estresse 8(1): 5-18. doi : 10.1080/10253890500044380 . PMID 16019594 ; Engelmann M, Landgraf R, Wotjak C (2004). "O sistema hipotalâmico-neurohypophysial regula o eixo hipotálamo-hipófise-adrenal sob estresse:. Um conceito antigo revisitado". Frente Neuroendocrinol 25 (3-4):. 132-49 doi : 10.1016/j.yfrne. 2004.09.001 . PMID 15589266 ; Courtney E. Detillion et al: facilitação Social da cicatrização de feridas , Psiconeuroendocrinologia, Volume 29, Issue 8, setembro de 2004, páginas 1004-1011, doi : 10.1016/ j.psyneuen.2003.10.003; Winberg S, Øverli Ø, Lepage O (2001). "Supressão de agressão em truta arco-íris (Oncorhynchus mykiss) por dietético L-triptofano.". J Exp Biol 204 (Pt 22):. 3867-76 PMID 11807104 ; Coplan JD, Mathew SJ, Smith EL, Trost RC, Scharf BA, Martinez J, Gorman JM, Monn JA, Schoepp DD, Rosenblum LA (Julho de 2001). "Efeitos do LY354740, um romance agonista metabotrópicos glutamatérgicos, sobre não-humano . primata eixo hipotálamo-hipófise-adrenal e função noradrenérgica ". CNS Spectr 6 (7):. 607-12, 617 PMID 15573025.
Contato:
Fones: 55 (11) 2371-3337 - 5572-4848 ou 98197-4706
Rua Estela, 515 - Bloco D - 12º andar - Conj. 121/122
Paraiso - São Paulo - SP - Cep 04011-002
e-mail: vanderhaagenbrasil@gmail.com
Rua Estela, 515 - Bloco D - 12º andar - Conj. 121/122
Paraiso - São Paulo - SP - Cep 04011-002
e-mail: vanderhaagenbrasil@gmail.com
Site Van Der Haagen Brazil
www.vanderhaagenbrazil.com.br,
http://drcaiojr.site.med.br/
http://dracaio.site.med.br/